The complexity of software systems today has amplified the importance of software testing as a scalable and efficient technique to discover defects. However, producing test cases by hand is tedious, expensive, and error-prone. Model-based software testing (MBT) enables automated test case generation from abstract models of the system under test to address this problem. However, for complex software systems, it is infeasible to explore and generate all the possible test cases for the software system under test. This means that a challenging decision needs to be made on how many test cases to generate. Also, it is a challenge for MBT to obtain desired test adequacy by generating a small test suite having few redundant test cases. Uncontrolled random approaches might result in test suites having redundant test cases which only cover few execution paths of the model and the SUT.
Our approach [1] considered test case generation as an exploration versus exploitation dilemma which is a classic reinforcement learning problem, and we addressed this dilemma by implementing a particular strategy of multi-objective multi-armed bandits with multiple rewards as a tool extension for the Modbat Tester [2]. After optimizing our strategy using the jMetal multi-objective optimization framework, the resulting parameter setting was then used by an extended version of the Modbat tool for model-based testing to generate optimal test cases. We experimentally evaluated our search-based approach on a collection of examples, including the ZooKeeper distributed service and PostgreSQL database system, by comparing it to the use of random search for test case generation.
Design
Reinforcement learning [3] is the subfield of machine learning devoted to studying problems and designing algorithms that analyze the exploration versus exploitation dilemma. The multi-armed bandit slot machine problem [4] is a well-established class of sequential decision problems in the context of reinforcement learning.
For our approach, we considered that the decisions required to select a possible test case to generate faces the exploration versus exploitation dilemma when searching/exploring the state space. In addition, we also considered that obtaining good and balanced results of the chosen test adequacy criteria with fewer generated test cases is a multi-objective optimization problem.
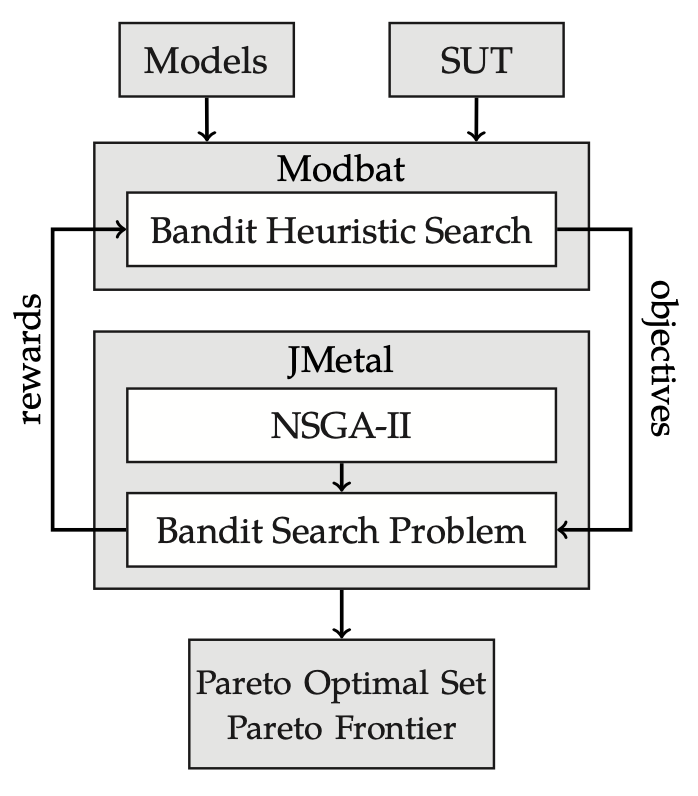
Therefore, we designed and implemented a bandit heuristic search strategy as a tool extension for the Modbat Tester. The strategy relies on the Upper Confidence Bounds (UCB) family [5] of algorithms to address the multi-armed bandit problem faced by test case generation. We then use the multi-objective optimization technique with the aid of the jMetal framework [6] and the NSAG-II genetic algorithm [7] to optimal our strategy based on the Pareto Efficiency [8] to obtain optimal test cases with considering the tradeoff of chosen test adequacy criteria. Its process is shown in the figure below. The generated Pareto Optimal Set has optimized parameter settings for the Modbat Tester to generate optimal test cases.
Implementation & development of software tools
-
Implemented a bandit heuristic search algorithm in Scala as a search-based test case generation tool extension included as a new feature for the Modbat Tester 3.4 release.
-
Developed a plot generator tool in Go to generate box plots for result data analysis of the evaluation.
-
Defined multi-objective bandit search problem in Java using an objective function, with the aid of the jMetal optimization framework.
-
The automated testing environment, test scripts, resulting data collection were developed using shell scripting, sed, and AWK programming languages.
Testing & Evaluation
We experimentally evaluated our approach on a collection of Modbat models from a training set including simple examples and the test set including two large examples which were the ZooKeeper distributed service and the PostgreSQL database system. The evaluation results showed that test cases generated using our search-based approach and optimization can obtain more predictable and better state/transition coverage, find failures earlier, and provide improved path coverage.
References
- R. Wang, C. Artho, L. M. Kristensen, and V. Stolz. Multi-objective Search for Model-based Testing. Submitted to The 20th IEEE International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability, and Security, Vilnius, Lithuania, IEEE, 2020.
- C. Artho, A. Biere, M. Hagiya, E. Platon, M. Seidl, Y. Tanabe, and M. Yamamoto, “Modbat: A model-based API tester for event-driven systems,” in Haifa Verification Conference, ser. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 8244. Springer, 2013, pp. 112–128.
- R. S. Sutton and A. G. Barto, Reinforcement learning: An introduction. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2011.
- D. A. Berry and B. Fristedt, “Bandit problems: sequential allocation of experiments (monographs on statistics and applied probability),” London: Chapman and Hall, vol. 5, pp. 71–87, 1985.
- P. Auer, N. Cesa-Bianchi, and P. Fischer, “Finite-time analysis of the multiarmed bandit problem,” Machine learning, vol. 47, no. 2-3, pp. 235–256, 2002.
- J. J. Durillo and A. J. Nebro, “jMetal: A Java framework for multi- objective optimization,” Advances in Engineering Software, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 760 – 771, 2011.
- K. Deb, S. Agrawal, A. Pratap, and T. Meyarivan, “A fast elitist non- dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II,” in International conference on parallel problem solving from nature. Springer, 2000, pp. 849–858.
- Y. Collette and P. Siarry, Multiobjective optimization: principles and case studies. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013.