Society is increasingly dependent on fault-tolerant cloud-based services which rely on the correctness and reliability of advanced distributed software systems and consensus protocols. The implementations of these systems require complex processing logic which in turn makes them challenging to implement correctly and also challenging to test in a systematic way. Model-based software testing (MBT) is a powerful approach for testing software systems. MBT enables automated test case generation from models, which can be used to investigate fault-tolerance and expose errors in the implementations of software systems.
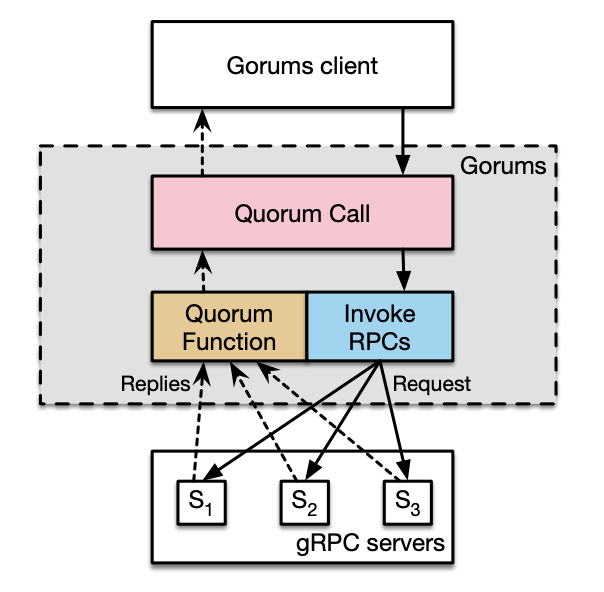
Our research goal was to provide an MBT approach for generating test cases to validate the correctness of quorum-based fault-tolerant distributed systems and consensus protocols implemented using the Gorums framework [1], in order to ensure the consistency and fault tolerance and in terms of concurrency, server failures, programming errors, and high code coverage. The Gorums framework is a novel framework relies on Quorums [2], the Google gRPC, and protocol buffers for building fault-tolerant distributed systems. The picture below shows the architecture of the Gorums framework.
Design
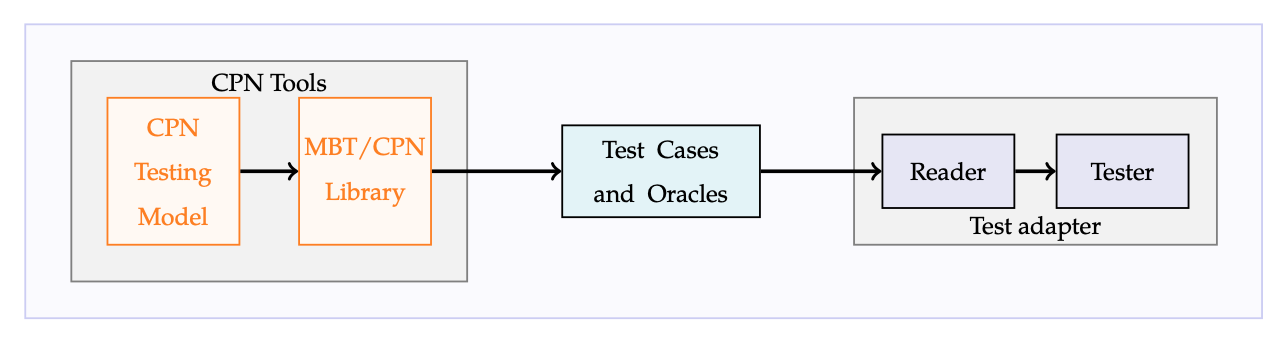
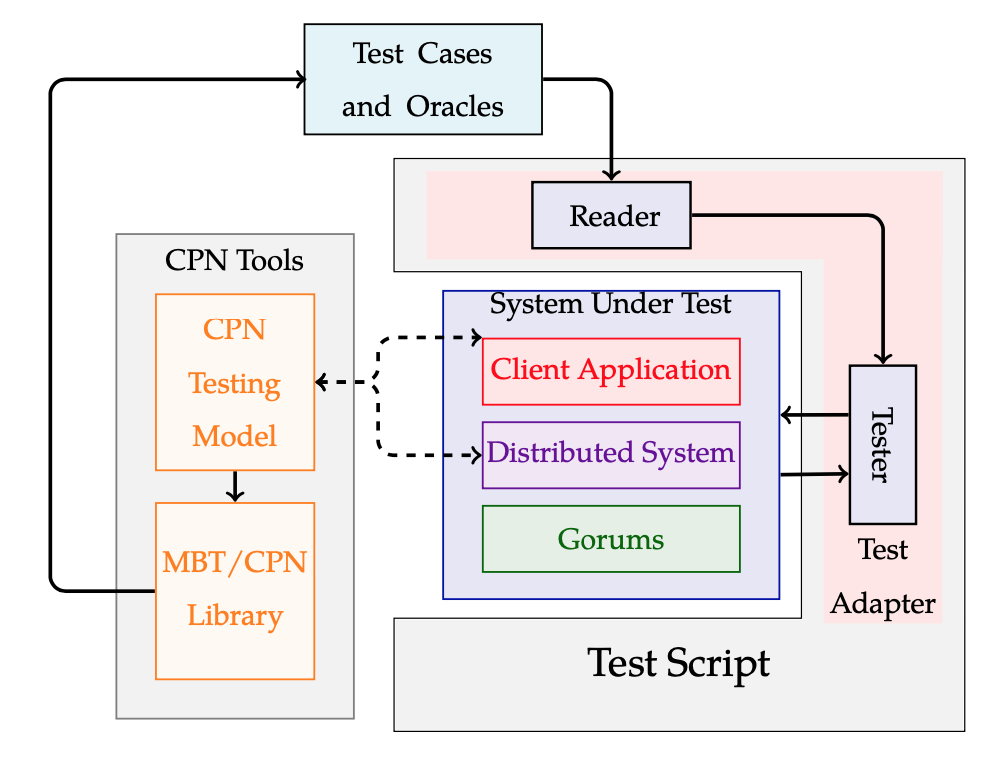
We designed a general MBT approach [3] and a QuoMBT framework [4] based on generating test cases from testing models created via Coloured Petri Nets (CPNs) [5] and CPN Tools [6]. QuoMBT enables testing of the Gorums middleware framework and quorum-based fault-tolerant distributed systems implemented via Gorums using automatically generated test cases. Our QuoMBT framework and MBT approach are shown in the figures below.
The QuoMBT framework
The MBT approach for Quorum-based fault-tolerant distributed systems and consensus protocols
Implementation & development of software tools
To apply our proposed MBT approach and QuoMBT testing framework,
-
two case studies were developed as systems under test including
- a distributed storage system (Github link) [7]
- a Paxos distributed consensus protocol (Github link) [8]
both implemented in the Go programming language and using the Gorums framework;
-
we also developed CPN testing models of these two distributed systems.
-
a CPN testing model for the distributed storage system:
the figures below briefly show the Clients module (left) and the server module (right) of the CPN model for the distributed storage service.
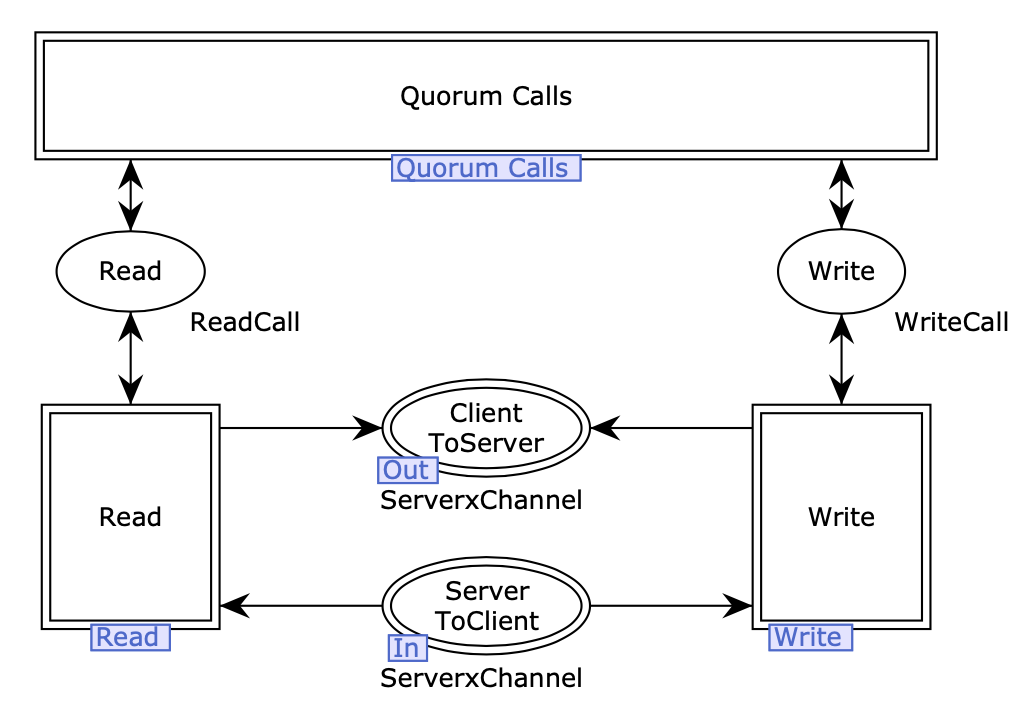
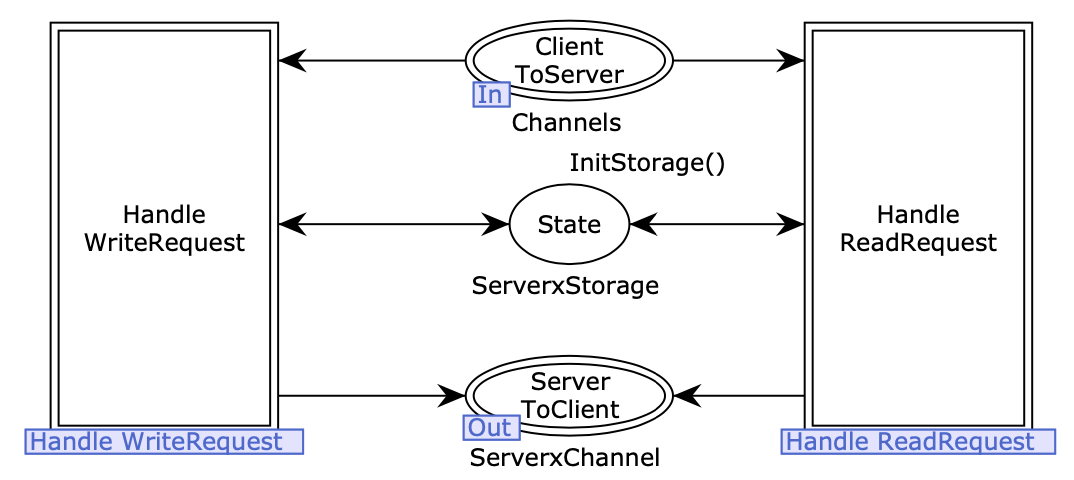
-
a CPN testing model for the Paxos distributed consensus protocol:
-
the figure below briefly shows the Paxos server replica module of the CPN model for the Paxos distributed consensus protocol. The module consists of three Paxos agent roles: the Proposer, Acceptor, and Learner.
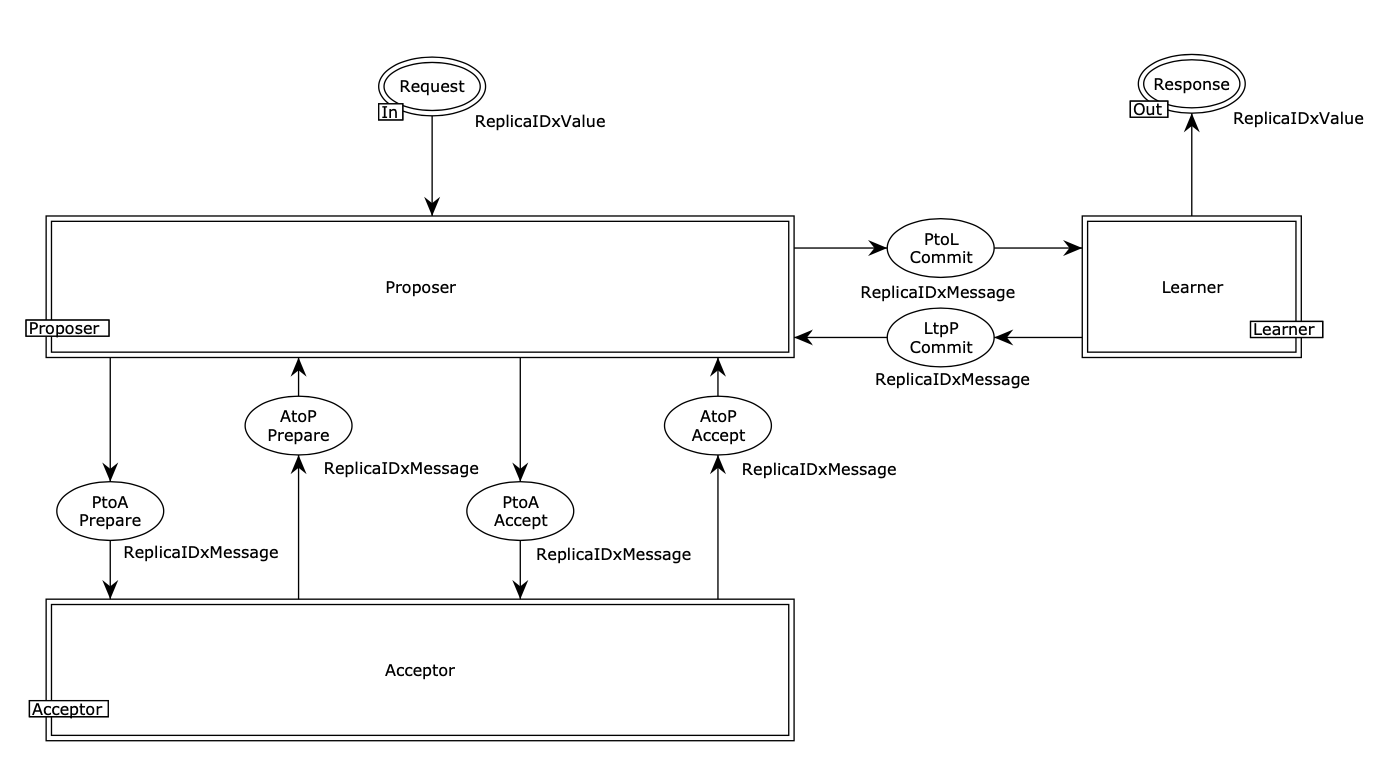
-
the automated testing environment and test scripts were developed using shell scripting.
-
in addition, we developed an MBT/CPN testing tool as an extension of CPN Tools for automated test case generation from CPN models and a test case execution engine in Go to use Go templates to automatically generate test adapters that perform automated test case execution. The details of these two tools will be discussed in another post.
Testing & Evaluation
The experimental evaluation showed that our MBT approach and the QuoMBT framework tested concurrent executions and fault tolerance, obtained high code coverage, and successfully detected programming errors in the Gorums middleware and distributed systems implemented based on the Gorums framework [3][4].
References
- Tormod Erevik Lea, Leander Jehl, and Hein Meling. Towards New Abstractions for Implementing Quorum-based Systems. In 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Jun 2017.
- M. Vukolić. Quorum Systems: With Applications to Storage and Consensus. Synthesis Lectures on Distributed Computing Theory, 3(1):1–146, 2012.
- R. Wang, L. M. Kristensen, H. Meling, and V. Stolz. Automated test case generation for the Paxos single-decree protocol using a Coloured Petri Net model. In Journal of Logical and Algebraic Methods in Programming, volume 104, pages 254–273, Elsevier Ltd, 2019.
- R. Wang, L. M. Kristensen, H. Meling, and V. Stolz. Model-Based Testing of the Gorums Framework for Fault-Tolerant Distributed Systems. In Transactions on Petri Nets and Other Models of Concurrency XIII, volume 11090 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 158–180, Springer International Publishing, 2018.
- K. Jensen and L. Kristensen. Coloured Petri Nets: A Graphical Language for Modelling and Validation of Concurrent Systems. Comm. ACM, 58(6):61–70, 2015.
- CPN Tools. CPN Tools homepage.
- Distributed Storage. Github link
- Paxos distributed consensus protocol. Github link
Other related publications
- R. Wang, L. M. Kristensen, H. Meling, and V. Stolz. Application of Model-based Testing on a Quorum-based Distributed Storage. In CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Petri Nets and Software Engineering (PNSE’17), volume 1846, pages 177–196, 2017.
- R. Wang, L. M. Kristensen, H. Meling, and V. Stolz. Model-based Testing of the Gorums Framework for Fault-tolerant Distributed Systems. In Proceedings of the 29th Nordic Workshop on Programming Theory (NWPT), Turku Center for Computer Science, Finland, 2017.